Self-Supervised Learning: The Engine Behind General AI
Towards AI
MAY 12, 2025
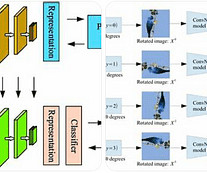
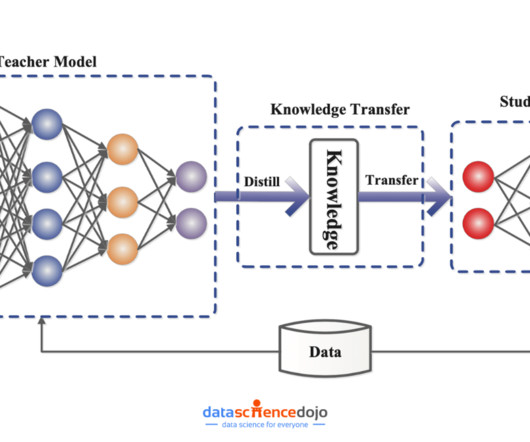
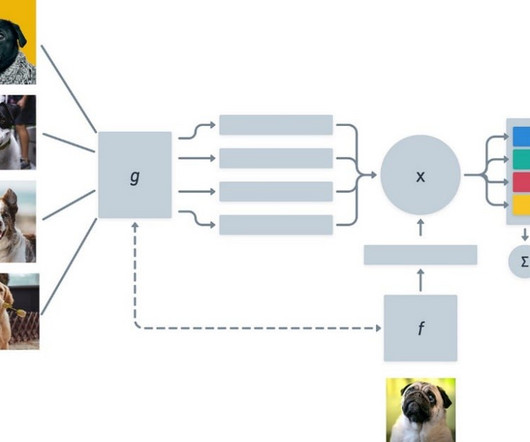
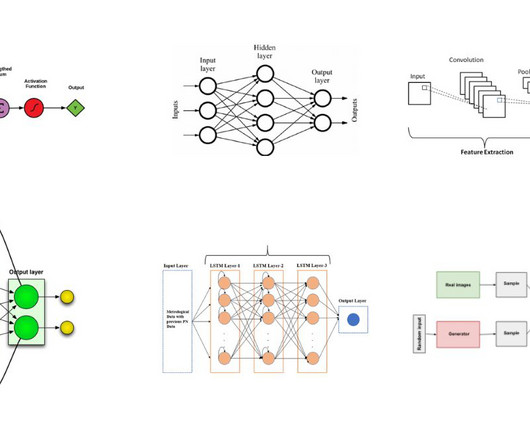
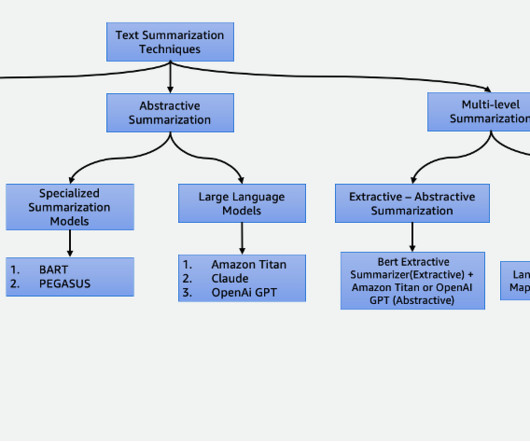
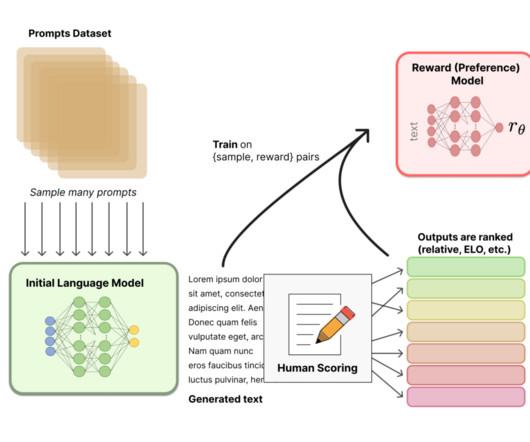
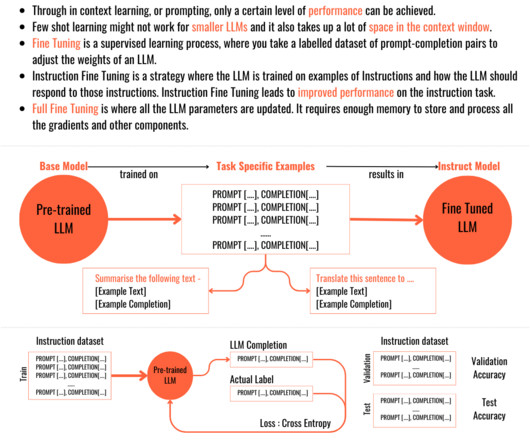
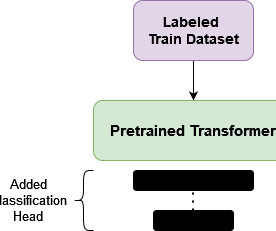
Typical SSL Architectures Introduction: The Rise of Self-Supervised Learning In recent years, Self-Supervised Learning (SSL) has emerged as a pivotal paradigm in machine learning, enabling models to learn from unlabeled data by generating their own supervisory signals. Core Techniques in SSL 1.






























Let's personalize your content