Predicting Heart Failure Survival with Machine Learning Models — Part II
Towards AI
JULY 19, 2023
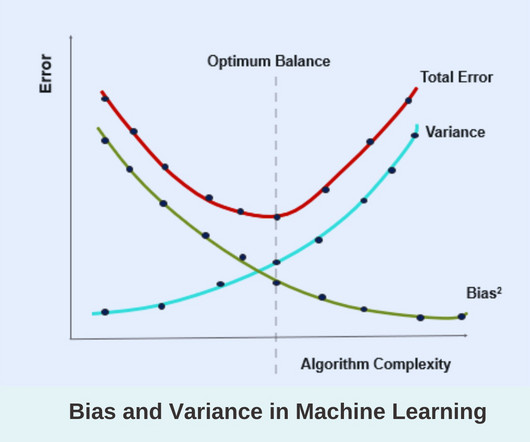
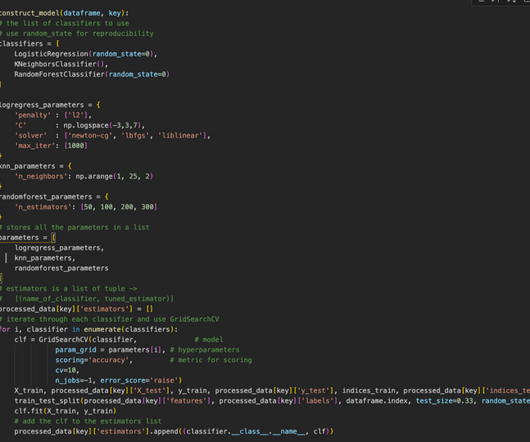
(Check out the previous post to get a primer on the terms used) Outline Dealing with Class Imbalance Choosing a Machine Learning model Measures of Performance Data Preparation Stratified k-fold Cross-Validation Model Building Consolidating Results 1. among supervised models and k-nearest neighbors, DBSCAN, etc.,





Let's personalize your content