It’s time to shelve unused data
Dataconomy
SEPTEMBER 22, 2023
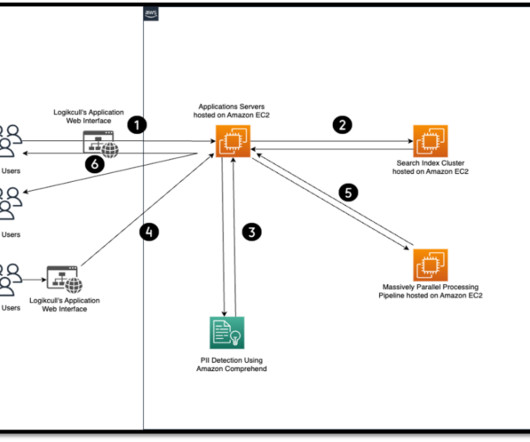
Artificial intelligence (AI) can be used to automate and optimize the data archiving process. There are several ways to use AI for data archiving. Consequently, this technology significantly simplifies the process of pinpointing specific files or information, saving time in finding the relevant information after data archiving.







Let's personalize your content